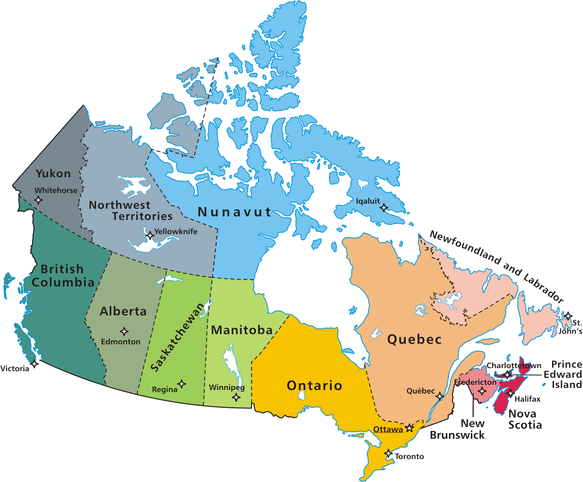
Canada is a country located in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometers (3.85 million square miles), making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Canada's southern border with the United States is the world's longest bi-national land border. Canada is sparsely populated, the majority of its land territory being dominated by forest and tundra and the Rocky Mountains. It is highly urbanized, with 82 percent of the 35.15 million people concentrated in large and medium-sized cities, many near the southern border. Its capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Canada's climate varies widely across its vast area, ranging from the arctic weather in the north to hot summers in the southern regions, with four distinct seasons.
Various indigenous peoples have inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years prior to European colonization. Beginning in the 16th century, the British and French established colonies, the first being the colony of Canada established by France in 1535. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, British North America gained and lost territory until, by the late 18th century, it controlled most of what comprises Canada today. On July 1, 1867, the colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia were federated to form the semi-autonomous federal Dominion named Canada. This began an accretion of provinces and territories to the Dominion to the present ten provinces and three territories forming contemporary Canada. Canada achieved independence gradually beginning with responsible government in the 1830s and culminating with the patriation of the Constitution in 1982. In 1931, Canada achieved near-total independence from the United Kingdom with the Statute of Westminster 1931, except for the power to amend its constitution.
Canada is a federal parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy, with Queen Elizabeth II being the head of state. The country is officially bilingual at the federal level. It is one of the world's most ethnically diverse and multicultural nations, the product of large-scale immigration from many other countries. Its advanced economy is the tenth-largest in the world, relying chiefly upon its abundant natural resources and well-developed international trade networks. Canada's long and complex relationship with the United States has had a significant impact on its economy and culture.
Canada is a developed country and has the fifteenth-highest nominal per capita income globally as well as the tenth-highest ranking in the Human Development Index. It ranks among the highest in international measurements of government transparency, civil liberties, quality of life, economic freedom, and education. Canada is a realm within the Commonwealth of Nations, a member of the Francophonie, and part of several major international and intergovernmental institutions or groupings including the United Nations, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, the G7 (formerly G8), the Group of Ten, the G20, the North American Free Trade Agreement and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum.
It is one of the ten provinces that, together with the three territories, make up the thirteen federal entities of Canada. Its capital is Victoria and its most populous city, Vancouver. It is located in the west of the country, bounded on the north by the Yukon and the Northwest Territories, on the east by Alberta, on the south by the United States, on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the northwest by Alaska (USA). With 4,648,055 habs as of 2017, it is the third most populated entity, behind Ontario and Quebec.
In 1866, Vancouver Island became part of the colony of British Columbia, and Victoria became the capital of the United Colony. In 1871, British Columbia became the sixth province of Canada. The economy is diverse, and the industries producing services represent the largest portion of the province's GDP. It is the terminus of two transcontinental railways and the site of 27 major maritime cargo and passenger terminals.
The province is rich in agriculture (particularly in the Fraser and Okanagan valleys), due to a milder climate near the coast and in certainly protected valleys of the south. Its climate encourages outdoor recreation and tourism, although its main economic support has long been the extraction of resources, mainly logging, agriculture and mining. Vancouver, the largest city in the province, serves as the headquarters for many natural resource companies based in the west. It also benefits from a strong housing market and a per capita income well above the national average. While the coast of British Columbia and some valleys in the south-central part of the province have a temperate climate, most of its landmass experiences a cold-winter-temperate climate similar to the rest of Canada.
The Northern Interior region has a subarctic climate with very cold winters. Vancouver's climate is by far the mildest winter climate in major Canadian cities, with night temperatures in January averaging above freezing. British Columbia has an economy based largely on its natural resources, mainly timber and mining. Employment in the agricultural sector has been decreasing, and new jobs are created mostly by the construction and services sector. Its film industry is the largest in Canada and the third in the continent, surpassed only by Los Angles and New York Even its most important city, Vancouver is known internationally as the Hollywood of the North. Economic activity related to mining, in particular, has fluctuated widely with changes in the prices of basic products over time, with documented costs for the health of the community. The most important mining products produced by the province are copper, gold, silver, lead, zinc, coal, oil and natural gas.
It is one of the ten provinces that, together with the three territories, make up the thirteen federal entities of Canada. Its capital is Edmonton and its most populous city, Calgary. It is located in the west of the country, bounded on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Saskatchewan, on the south by the United States and on the west by British Columbia. With 4 067 175 inhabitants. in 2016 it is the fourth most populated entity, behind Ontario, Quebec and British Columbia.
Alberta has one of the strongest and most influential economies in Canada. The province is a large producer of oil and natural gas. Alberta produces about 70% of Canada's oil and natural gas. A large part of these natural resources is exported to the United States. In addition, agriculture, manufacturing, finance and tourism are also of great importance in the economy of the province.
The primary sector is responsible for 3% of Alberta's GDP. Agriculture and livestock - which were previously Alberta's main sources of income - together account for 2.92% of the province's GDP, and employ approximately 70,000 people. Alberta has about 55 thousand farms, which cover about 35% of the province. Fishing and forestry together account for 0.08% of the province's GDP and employ about 1,500 people together. Alberta is a national leader in the area of agriculture. The province has the largest cattle herds in Canada and one of the largest herds in North America. Alberta has a total of about 5 million heads of cattle. About half of all Canadian beef is produced in Alberta. The province is also the largest producer of bison meat in Canada. Alberta also has considerable herds of sheep, which are used mainly for wool production. Alberta is the largest national wheat producer in Canada, and one of the largest in the world. It is also a large rapeseed producer. On top of that, Alberta is a national leader in beekeeping.
Alberta's secondary sector accounts for 36% of GDP. The mining industry - based mainly on the extraction of oil, tar, coal and natural gas - corresponds to 19% of GDP, being the province's largest source of income. Mining employs a total of more than 85 thousand people. Alberta's other mineral resources are sulphur and salt. The manufacturing industry corresponds to 10% of the GDP of the province, employing about 140 thousand people. The products manufactured annually in the province have a total value of more than 14 billion Canadian dollars. The main products manufactured in Alberta are petroleum products, chemical products, processed foods and products derived from metals and wood. The construction corresponds to 7% of the GDP of the province, employing more than 130 thousand people. Alberta is the largest producer of fossil fuels in Canada; it produces more than 70% of the national production. Also one of the largest producers in the world. On top of that, Alberta has the largest bitumen reserves in the world. In fact, it is estimated that these bitumen reserves contain more than 1.6 trillion barrels of oil - more than in the rest of the world. Until the 1980s, the refinement of bitumen for the collection of oil was a very expensive task. However, several oil companies developed technologies and refining methods that reduced the production costs of the oil obtained through these bitumen reserves. On top of that, the recent increases in the price of a barrel of oil made the refining of bitumen in oil a particularly lucrative activity. Alberta is expected to produce more than 10% of North America's oil alone in 2010. The state's industrial capital is Edmonton, where most of the province's oil refineries are based. The total value of the natural resources produced in Alberta corresponds to 60% of the value of all natural resources extracted throughout Canada.
The tertiary sector of Alberta corresponds to 61% of the GDP of the province. Calgary hosts the main oil companies in the country (and other multinationals installed in the country), as well as various financial and telecommunications companies. The community and personal services correspond to 20% of the GDP of the province and employ about 602 thousand people. The financial and real estate services correspond to 16% of the GDP of the province and employ approximately 79 thousand people. Wholesale and retail trade corresponds to 9% of Alberta's GDP, employing 159,000 people. Transports and telecommunications correspond to 11% of Alberta's GDP, employing approximately 630 thousand people. Government services employ approximately 62,000 people and account for 4% of the province's GDP. Public utilities correspond to 3% of Alberta's GDP and employ about 12.5 thousand people. Nearly 50% of the electricity produced in Alberta is generated in coal-fired power plants, and 32% is produced in natural gas thermoelectric plants.
It is a province of western Canada, is the central province of the Canadian Prairies. Its capital is Regina and its most populous city is Saskatoon.
Saskatchewan borders on the west with Alberta, on the north with the Northwest Territories, on the east with Manitoba, and on the south with the US states of Montana and North Dakota. Saskatchewan is the only Canadian province in which none of its borders correspond to physical geographical features. It is also one of only two provinces with no access to the sea, together with Alberta.
Most of its population is concentrated in the southern part of the province. Agriculture is a fundamental part of the economy of Saskatchewan, especially wheat, from which 45% of all Canada is harvested. Mining is another fundamental source of the economy of the province. Saskatchewan is the largest producer of uranium in the world.
The highest point of the province, 1,468 meters high, is located in the Colinas del Ciprés. The lowest point, at 213 meters, is on the shore of Lake Athabasca at the northern end. The province has nine different watersheds formed by several rivers that flow into the waters of the Arctic Ocean, Hudson Bay and the Gulf of Mexico.
The economy of Saskatchewan is traditionally agricultural; However, the emerging diversification has meant that now this activity, together with afforestation, fishing and hunting, constitute only 6.8% of the province's GDP. Wheat is the most common crop, and perhaps the only representative of Saskatchewan, but others are also present such as rapeseed, flax, rye, oats, peas, lentils, millet, and barley. Also, mining is of vital importance for the province. Saskatchewan is the world's leading exporter of potash. In the northern area, forestry activity regains some relevance.
Saskatchewan is also the largest supplier of uranium in the world and supplies most of the Western Hemisphere. The industry of this mineral is followed closely by the provincial government that endorses its quotation in the international market.
It is one of the ten provinces that, together with the three territories, make up the thirteen federal entities of Canada. Its capital and the most populous city is Winnipeg. It is located in the centre of the country, bordering northwest with Northwest Territories, north with Nunavut, northeast with Hudson Bay, east with Ontario, south with the United States and west with Saskatchewan.
The province has an area of 649,950 km² in which prairies and a continental climate predominate, with thousands of lakes and many rivers. The economy of the territory is based on agriculture that is practiced in the fertile areas of the south and the west of the province. Other important economic sectors are transport, manufacturing, mining, forestry, energy and tourism.
The capital and largest city of Manitoba in Winnipeg, the eighth city of Canada in population and home to 60% of the inhabitants of the province. Winnipeg is the seat of the provincial government and in it are the Legislative Assembly of Manitoba and the Court of Appeal of Manitoba, which is the highest judicial body. Four of the five universities in Manitoba, their professional sports teams and most of the cultural activities are in Winnipeg.
The fur traders first came to the territory of present-day Manitoba at the end of the 17th century and the area became the heart of Rupert Land, owned by the Hudson Bay Company. Manitoba reached the category of a province of Canada in 1870, after the Red River Rebellion. In 1919 a general strike took place in Winnipeg and shortly after the region was affected by the economic crisis known as the Great Depression. These events led to the creation of what would eventually become the New Democratic Party of Manitoba, one of the main political parties in the province.
The economy is based mainly on agriculture, tourism, energy, oil, mining and forestry. Agriculture is vital and is found mainly in the southern half of the province, with cereals as the dominant crop. About 12% of agricultural land in Canada is located in Manitoba. The most common type of farm found in rural areas is livestock (34.6%), followed by a variety of grains (19.0%) and oilseeds (7.9%).
Manitoba is the largest national producer of sunflower seeds and dried beans and one of the main sources of potatoes. Portage la Prairie is a processing centre for large potatoes and is home to the McCain Foods and Simplot plants, which offer McDonald's, Wendy, and other commercial chains. Can-oat milling, one of the largest oat factories in the world, also has a plant in the township.
It is one of the ten provinces that, together with the three territories, make up the thirteen federal entities of Canada. It is home to the largest Canadian city, Toronto, and Ottawa, the capital. It is located in the centre-east of the country, bounded on the north by Hudson Bay, on the east by Quebec, on the south by the Great Lakes and the Niagara River that separate it from the United States, and on the west by Manitoba. The southern region of Ontario is home to the southernmost point in all of Canada.
The main source of income for Ontario is the industry. The value of industrial products produced in Ontario is greater than the sum of the total value of industrial products manufactured in all other provinces and territories of Canada. The strength of its manufacturing industry earned it the nickname Manufacturing Heartland of Canada. The province stands out mainly for its strong automotive industry the most competitive of the entire American continent with the exception of Michigan of the United States. Other important sources of income are tourism and the provision of financial and real estate services.
Ontario is one of the richest and most economically prosperous national subdivisions of North America, thanks to its strong and varied economy, its gradually growing population and the existence of skilled labour.
The primary sector is responsible for 1.5% of Ontario's GDP. Currently, it has about 67 thousand farms, which occupy about 5% of the province. Agriculture and livestock together employ about 140 thousand people and correspond to 1% of GDP. The decrease in the number of farms in the last decades caused the average size of Ontario farms to grow. Forestry corresponds to about 0.5% of GDP, employing approximately 90 thousand people. Fishing corresponds to less than 0.01% of GDP, employing close to a thousand people.
The secondary sector is responsible for 27.5% of the province's GDP. The manufacturing industry is responsible for 22% of provincial GDP, employing approximately 1.1 million people. The industry is the province's largest source of income. Ontario's manufacturing industry employs more than half of all industrial workers across Canada. The main products manufactured in Ontario are automobiles, trucks and similar products, electronic products such as televisions and computers, steel (Hamilton is one of the largest steel centres in the world), food products and chemical products.
The construction industry employs approximately 325,000 people and is responsible for approximately 4.5% of the province's GDP. And mining, formerly one of the province's main sources of income, has progressively declined with the diversification of Ontario's economy and with the increasing modernization in this area in recent decades - currently, mining corresponds to only 1 % of the GDP of Ontario, employing about 35.2 thousand people. The province has large reserves of nickel - an eighth of the world's nickel is produced in Ontario - cobalt, copper, gold, silver and zinc.
The tertiary sector accounts for 71% of all of Ontario's GDP. Community and personal services correspond to 23% of provincial GDP and employ more than 2.25 million people. Financial and real estate services employ 390,000 people and are responsible for 22% of Ontario's GDP. Toronto is the financial capital of Canada. Wholesale and retail trade accounts for 15% of the province's GDP and employs approximately 1.4 million people. Transport and telecommunications employ approximately 46 thousand people and correspond to 8% of the province's GDP. Government services correspond to 5% of the GDP of Ontario and employ 275 thousand people. Finally, public services correspond to 3% of the GDP of the province, employing about 560.3 thousand people. Nearly 50% of the electricity generated in Ontario is produced in nuclear power plants, 25% in hydroelectric power plants and most of the rest is produced in thermoelectric plants in general (which can use coal, oil or natural gas as fuel).
It is one of the ten provinces that, together with the three territories, make up the thirteen federal entities of Canada. Its capital is the homonymous Quebec and its most populated city, Montreal. It is located in the east of the country, bordering northwest and north with Hudson Bay and the Hudson Strait, respectively, which separate it from Nunavut, northeast with Newfoundland and Labrador, east with the Gulf of St. Lawrence and New Brunswick, to the southeast with the San Lorenzo River that separates it from the United States, and to the south and southwest with Ontario.
Because of its language, culture and institutions, it forms a nation within Canada, unlike the other provinces, Québec has the only official language in French and is the only majority French-speaking region in North America.
On November 27, 2006, the Canadian parliament, with the support of the ruling party, recognized the Quebecois as a nation within Canada united in an attempt to appease the secessionist desires of the independence parties, although it was in a cultural and social sense Not legal.
The province of Quebec is highly industrialized and the territory abounds in natural resources, among which are minerals, large coniferous forests that nourish an important timber industry or lakes, rivers and other streams that produce hydroelectric energy not only for domestic consumption but also for export to the United States.
The San Lorenzo Valley is a very fertile agricultural region. Having a large livestock hut, it produces varied dairy products and meat, and in its fields, excellent fruits and vegetables are harvested. It highlights to a large extent the production of maple sugar, of which the province of Quebec is the world's leading producer.
Also sometimes called New Brunswick and commonly abbreviated NB, it is one of the ten provinces that, along with the three territories, make up the thirteen federal entities of Canada. Its capital is Fredericton and its most populous city, Moncton. It is located in the east of the country, bounded on the north by the Gulf of San Lorenzo that separates it from Prince Edward Island, on the east by the Bay of Fundy that separates it from Nova Scotia, on the south by the United States and on the west by Quebec.
New Brunswick is part of the Maritime Provinces and the Atlantic Provinces and is the only Canadian province that has English and French as official languages.
Most of New Brunswick is covered by forests. Forestry is one of the main sources of income in the province. New Brunswick is one of the largest wood producers in Canada, as well as the largest producer of newspaper in the country. The most important sources of income for New Brunswick are manufacturing, tourism, forestry, mining and fishing.
Together with Nova Scotia, Ontario and Quebec, New Brunswick is one of the four original provinces of the Canadian Confederation, created on July 1, 1867.
The primary sector accounts for 5% of New Brunswick's GDP. Agriculture and livestock together account for 2% of the GDP of the province and employ approximately 6.1 thousand people. New Brunswick owns about 3.4 thousand farms that cover 5% of the province. The main products of the primary sector in New Brunswick are potatoes, ornamental flowers and meat and milk. Forestry contributes 2% of the GDP of the province, employing about 7 thousand people. Fishing accounts for about 1% of GDP and employs about 3,000 people. The annual value of the fishing captured in the province is approximately 175 million Canadian dollars.
The secondary sector contributes 25% of New Brunswick's GDP. The manufacturing industry contributes 14% of the GDP of the province and employs approximately 41 thousand people. The construction sector accounts for 5% of the GDP of the province and employs about 19.6 thousand people. Mining contributes 2% of GDP and employs approximately 3 thousand people. The main natural resources extracted in New Brunswick are lead, copper, silver, zinc, cadmium, bismuth, gold and coal.
The tertiary sector accounts for 70% of New Brunswick's GDP. The services represent 22% of the GDP of the province and employ about 127.3 thousand people. Financial and real estate services employ approximately 12.7 thousand people and account for more than 22% of New Brunswick's GDP. Wholesale and retail trade accounts for 11% of the province's GDP and employs approximately 55.1 thousand people. Transport and telecommunications account for 10% of GDP and employ approximately 32.2 thousand people and government services 10% of the GDP of the province, employing approximately 22.9 thousand people. Public services account for 4% of the GDP of the province and employ approximately 4.3 thousand people.
It is one of the ten provinces that, together with the three territories, make up the thirteen federal entities of Canada. Its capital and the most populated city is Halifax. Located in the extreme east of the country, it is formed by the homonymous peninsula and the island of Cape Breton in the north end of this one. The peninsula is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, except for the Isthmus of Chignecto, which links it to New Brunswick, and the Northumberland Strait, which separates it from Prince Edward Island.
It is part of the Maritime Provinces. Its capital is a very important part of North America. Fishing and tourism are vital for the economy of the province.
Nova Scotia's economy is currently based on the service sector and the industrial sector, although the primary sector continues to maintain its presence.
In the primary sector, as regards agriculture, the production of fruit, especially apples, and potatoes stand out. In the cattle ranch, poultry and pigs are present, together with a cattle hut that generates dairy products.
There is also an active forestry-type industry, dedicated to the exploitation of the forests of the territory.
On the other hand, fishing for lobsters, bivalves (especially scallops) or cod, is also important.
It also has an active industry, related to fishing activities and the food industry in general, but also paper industry, transport equipment.
Tourism has gained increasing importance throughout the second half of the 20th century.
It is one of the ten provinces that, together with the three territories, make up the thirteen federal entities of Canada. Its capital and the most populated city is Charlottetown. Located to the east of the country, it is an island surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean and separated from New Brunswick by the Northumberland Strait.
Its capital, Charlottetown, is known as the cradle of the Canadian Confederation, although the province was not associated with the Confederation until later. Recently it was united to the American continent by the bridge of the Confederation.
The economy of Prince Edward Island is based mainly on agriculture, tourism and fishing. All these activities have wide variations throughout the year and are susceptible to external impacts such as for example, natural disasters and economic depressions. This province is extremely poor in natural resources, such as mineral mines, however, there are still not determined quantities of natural gas in its eastern part.
Agriculture is the main source of income for the economy of the province since it was colonized by the English - currently, the potato is the most cultivated vegetable in the province. Prince Edward Island is the largest producer of potatoes in Canada - it is responsible for one-third of Canada's annual production. About 1.3 billion kilos of potatoes are produced annually in the province, which is also a large producer of potato seeds, which are exported to more than 20 countries around the world.
Tourism is the second largest source of income of Prince Edward Island, having exceeded in importance to fishing in the mid-twentieth century. The main tourist attractions are its beaches, golf courses and local attractions and events. The most dynamic season is summer - months of July and August - despite an increase in the number of American tourists in September and October in the province (as well as in New Brunswick and Nueva Escocia), the tourist season is being extended to winter months.
Fishing is still the third largest source of income for Prince Edward Island; however, the province is less dependent on the fishing industry than other Canadian provinces located on the Atlantic coast (New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Newfoundland and Labrador). The lobster catch is the island's biggest fishing activity, which takes place in May and September. Due to the fact that the province is covered by oceanic ice during the winter months, fishing is limited to the summer months, the end of spring and the beginning of autumn.
The gross domestic product of British Columbia is more than 2.8 billion Canadian dollars per year. The primary sector contributes 5% of the GDP of Prince Edward Island. Agriculture and livestock represent together 5% of the GDP of the province and employs approximately 4.6 thousand people. Prince Edward Island has about 2,000 croplands, which cover approximately half of the province. Only Saskatchewan has a greater percentage of its territorial extension covered by farmland. The fishing represents 4% of the GDP of the province and employs approximately 2 thousand people. Forestry represents 1% of the GDP of the province, employing about 700 people.
The secondary sector represents 16% of the GDP of Prince Edward Island. The total value of the products manufactured in the province is 275 million Canadian dollars. The main industrial products manufactured in the province are mainly industrialized foods, partly associated with the province's fishing industry. The manufacturing industry represents 10% of the GDP of Prince Edward Island and employs approximately 6.5 thousand people. The construction industry represents 5% of the province's GDP and employs about 3.8 thousand people. The economic contribution of the mining exploitation of the province is negligible. The only natural resource present in the province of important use for man is the small reserves of natural gas.
The tertiary sector represents 76% of the GDP of Prince Edward Island. Personal and community services represent 25% of the GDP of the province and employ about 24.1 thousand people. Financial and real estate services employ approximately 2.2 thousand people and represent more than 20% of the GDP of Prince Edward Island. Government services represent 13% of the province's GDP, employing approximately 5.6 thousand people. The wholesale and retail trade represents 11% of the province's GDP and employs approximately 9.9 thousand people. Transport and telecommunications represent 7% of GDP and employ about 5 thousand people, and public utilities represent 1% of the province's GDP, employing close to 100 people. The province generates barely 40% of the electricity it consumes, 5% in coal thermoelectric plants, and 35% in wind power plants. The other 60% needs to be purchased from New Brunswick.
It is one of the ten provinces that, together with the three territories, make up the thirteen federal entities of Canada. Its capital is San Juan de Terranova. Located in the northeast of the country, it is formed by two different areas: Labrador located on the peninsula of the same name, bounded on the north by the sea of the same name and on the west and south by Quebec and Newfoundland, an island located on the eastern edge, which borders on the north and east with the Atlantic Ocean, and to the west with the Gulf of San Lorenzo.
For many years, Newfoundland and Labrador had a depressed economy. After the collapse of the cod fishery, the province registered high unemployment rates and the population decreased by around 60,000. However, the growing mining industries and the recent discoveries of offshore oil have pushed the provincial economy.
The GDP reached 28.1 billion Canadian dollars, compared to 25.0 billion in 2009. GDP per capita in 2008 was 61,763 Canadian dollars, much higher than the national average. Services provide more than 60% of GDP, especially financial services, healthcare and public administration. Other important industries are mining, oil production and manufacturing.
Mining is focused on obtaining iron, nickel, copper, zinc, silver and gold.
The forestry industry is important since it produces 462,000 tons of wood per year. The value of newsprint exports is very variable from year to year, depending on the world market price. Wood is produced by numerous mills in Newfoundland.
Aquaculture is a new industry for the province, which in 2006 produced more than 10,000 tons of Atlantic salmon, mussels and rainbow trout of more than $ 50 million. In Newfoundland it is limited to areas south of San Juan, near Deer Lake and in the Codroy Valley. They grow mainly potatoes, turnips, carrots and cabbage is grown for local consumption. Wild blueberries and blackberries are grown for commercial purposes and used in jams and wine. Livestock is reduced to aviculture and milk production. Apart from shellfish processing, papermaking and oil refining, the industry is complemented by small food-producing industries, the production of beer and other beverages, and footwear. Tourism is also growing.
It is one of the three territories that, together with the ten provinces, make up the thirteen federal entities of Canada. Its capital is Whitehorse. It is located in the northwest corner of the country, bounded on the north by the Arctic Ocean, on the east by the Northwest Territories, on the south by British Columbia and on the west by Alaska (United States). With 31,530 habs. in 2008 it is the second least populated entity - ahead of Nunavut - and with 0.06 hab / km², the third least densely populated, ahead of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut, the least densely populated.
The ridge of the Mackenzie Mountains shapes much of the eastern border.
The etymology of its name comes from a local aboriginal language, the Gwich'in, and means "big river". The territory is famous among other things for having been the scene of the Klondike Gold Rush, a historical event that occurred in 1897 and that was of great importance for the region.
The economy is based on mineral resources (lead, zinc, silver, gold, asbestos, copper, tungsten, jade and barite). The manufacturing industry, including furniture, clothing and crafts, follows in importance, along with hydroelectricity.
The main attraction of the Yukon is its almost virgin nature and the tourism of the place depends to a great extent on this, there are many suppliers of organized equipment and guides available to hunters and fishermen and nature lovers of all kinds. Sports enthusiasts can paddle in lakes and rivers with canoes and kayaks, take trips or walks, ski or snowboard in an organized environment or access by snowmobile, climb the highest peaks in Canada or have a small hike through the mountains, or try ice climbing and dog sledding.
Yukon also has a wide range of cultural and sports activities that attract artists, participants and tourists from all over the world.
It is one of the three territories that, together with the ten provinces, make up the thirteen federal entities of Canada. Its capital and most populated city is Yellowknife. It is located, as the name suggests, in the northwest of the country, bounded on the north by the Arctic Ocean, on the east by Nunavut, on the southeast by Manitoba, on the south by Saskatchewan, Alberta and British Columbia, and on the west by Yukon.
Some of its geographical features include the vast Great Bear Lake and the Great Slave Lake, as well as the immense Mackenzie River and the canyons of the Nahanni National Park, a park qualified as Canada's Natural Protected Area and declared a World Heritage Site by the Unesco The islands of the territory in the Canadian Arctic archipelago include: Banks Island, Borden Island, Prince Patrick Island, and parts of Victoria Island and Melville Island.
The territory enjoys vast geological resources, including diamonds, gold, and natural gas. In particular, the diamonds of the Northwest Territories are offered as an ethical alternative that relieves the risks of supporting conflicts to acquire the so-called "war diamonds".
It is one of the three territories that, together with the ten provinces, make up the thirteen federal entities of Canada. Its capital is Iqaluit. It is located in the north of the country, bounded on the north by the Arctic Ocean, on the northeast by Baffin Bay that separates it from Greenland, on the east by the Atlantic Ocean and Hudson Bay, on the south by Manitoba, on the southwest by Saskatchewan and to the west with Northwest Territories.
Nunavut was separated from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, according to the boundaries set in advance in 1993. These borders recognized the jurisdiction of Nunavut over almost all the Arctic Islands of Canada (Ellesmere, Baffin, Devon, Southampton and the eastern half of Victoria and Melville), as well as over the central coastal area of Canada over the Arctic Ocean and all the islands of Hudson Bay.
Its inhabitants called Nunavutensinos (Nunavummiut, singular Nunavummiuq) - are distributed in almost thirty villages or smaller towns. One of them is Iqaluit, the capital, located on the island of Baffin, formerly called Frobisher Bay.
The economy is based on mineral resources, especially gold, lead and zinc. There are also many diamonds. Hunting and fishing are other important activities. Tourism is constantly growing.
Katapulta is the project that will help you to visit, study, work or live in Canada.
We share information on many cities in Canada, how to write a proper resume, the process of obtaining or getting certain documents for Canada, myths and facts and much more information coming from experience or common questions.